The following press release was published on July 6, 2023. View the original Tenovi press release at PR Newswire.
Introducing Tenovi Cellular-Connected Infrared Thermometer: Remote Patient Monitoring with FDA-cleared Advanced Temperature Monitoring Technology
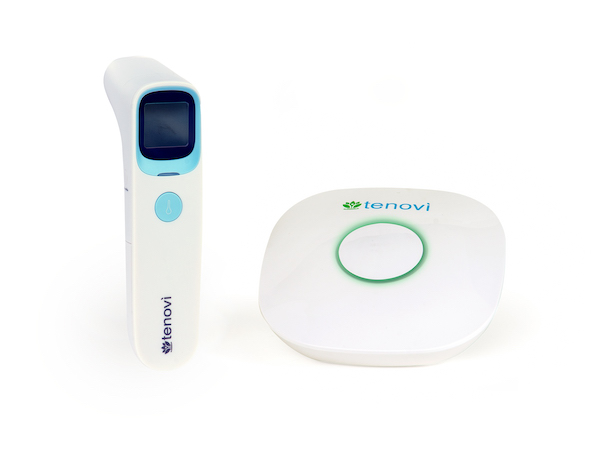
Leading remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution innovator Tenovi has released its cellular-connected Infrared Thermometer. Combined with the Tenovi Cellular Gateway, the FDA-cleared RPM medical device allows patients to automatically transmit real-time temperature readings to clinicians.
“Tenovi’s Infrared Thermometer integration with the Tenovi Cellular Gateway enables healthcare providers to utilize real-time temperature data to make better decisions quicker,” said Nizan Friedman, PhD., founder and CEO of Tenovi.
A remote patient monitoring thermometer is crucial in early infection detection, particularly for sepsis, where timely treatment is crucial. The Tenovi Infrared Thermometer provides a 1-second measurement that tracks body temperature remotely, providing alerts to healthcare professionals for prompt and effective care of patients’ postoperative and chronic care applications.
Tenovi’s dual-mode advanced infrared temperature technology offers eardrum and no-touch forehead modes, ensuring accurate temperature measurements in adults and children with an impressive accuracy of +/-0.3°C (+/-0.6°F).
“We are dedicated to developing innovative solutions that enhance patient adherence, reduce hospital readmission rates, and meet the growing demand for seamless integration with diverse software and services for chronic care, telehealth, and remote patient monitoring companies,” added Friedman.
About Tenovi
Tenovi is a data aggregation and automation platform connecting medical device manufacturers with remote patient monitoring companies. They provide a growing number of medical device point solutions that connect with their proprietary cellular gateway to automate the transfer of patient vitals. Their API-driven fulfillment and automation services enable seamless deployment of remote patient monitoring programs.
1 Ferrer, R., Martin-Loeches, I., Phillips, G., Osborn, T. M., Townsend, S., Dellinger, R. P.,
Artigas, A., Schorr, C., & Levy, M. M. (2014). Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Critical Care Medicine, 42(8), 1749–1755. https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000000330
2 Liu, V. X., Fielding-Singh, V., Greene, J. D., Baker, J. M., Iwashyna, T. J., Bhattacharya, J., & Escobar, G. J. (2017). The timing of early antibiotics and hospital mortality in sepsis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 196(7), 856–863. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201609-1848OC